Managing a project involves a delicate balance of coordination, communication, and execution. To ensure that all stakeholders are on the same page and projects stay on track, it is crucial to have a clear and effective way to communicate the current status of a project. This is where a progress report comes in.
A progress report allows project managers to detail what tasks have been completed, what is currently in progress, and any potential issues that may arise. By providing stakeholders with this information, they can evaluate if the project is on track to meet its goals and deadlines and make informed decisions about next steps.
What is a Progress Report?
A progress report is a document that summarizes the current status of a project. It provides an overview of the tasks that have been completed, the tasks that are currently in progress, and any potential issues or roadblocks that may affect the project’s timeline or success.
This report is typically shared with all project stakeholders, including team members, clients, and executives, to keep everyone informed and aligned.
Why Use a Progress Report?
A progress report serves several important purposes in project management:
- Communication: A progress report ensures that all stakeholders are aware of the project’s status and can easily understand the progress made.
- Transparency: By sharing the progress report, project managers demonstrate transparency and build trust with stakeholders.
- Evaluation: The report allows stakeholders to evaluate if the project is on track and identify any potential issues that need to be addressed.
- Decision Making: With the information provided in the progress report, stakeholders can make informed decisions about the next steps and allocate resources accordingly.
- Accountability: The progress report holds team members accountable for their assigned tasks and deadlines.
How to Create a Progress Report
Creating a progress report involves several key steps:
1. Define the Key Elements
Start by identifying the key elements that should be included in the progress report. This typically includes the project name, a summary of the overall progress, a breakdown of completed tasks, tasks in progress, and any potential issues or risks.
2. Gather the Necessary Information
Collect all the relevant data and information needed for the progress report. This may include updates from team members, task completion percentages, and any issues or roadblocks that have been encountered.
3. Structure the Report
Organize the information clearly and logically. Use headings, subheadings, and bullet points to make the report easy to read and navigate. Consider using visual elements such as charts or graphs to present data in a more visually appealing way.
4. Provide Context and Explanation
Ensure that each section of the progress report provides sufficient context and explanation. This allows stakeholders to understand the current status of the project and any potential issues that may arise.
5. Review and Revise
Before finalizing the progress report, review it carefully to ensure accuracy and clarity. Make any necessary revisions or additions to improve the report’s effectiveness.
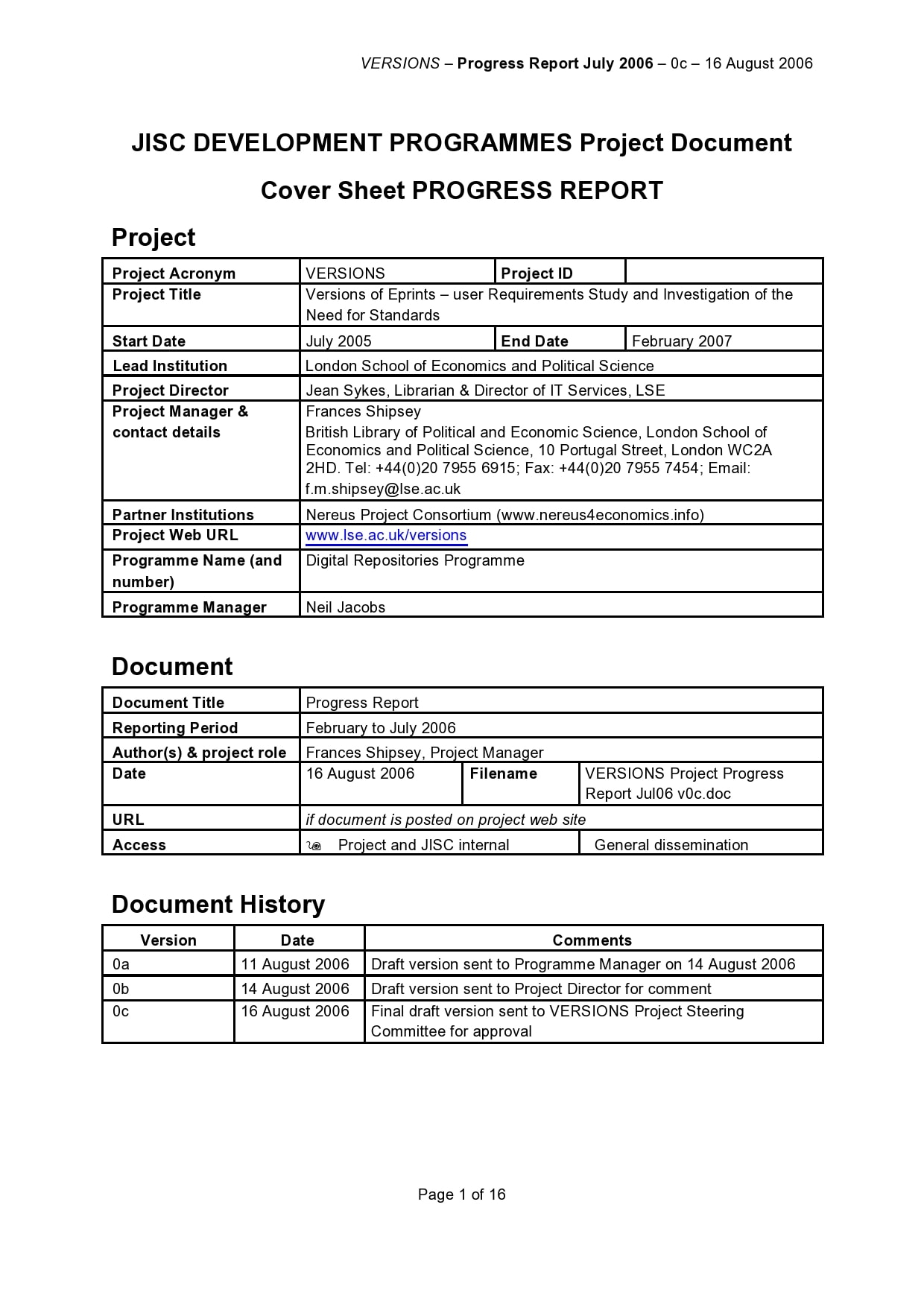
Examples
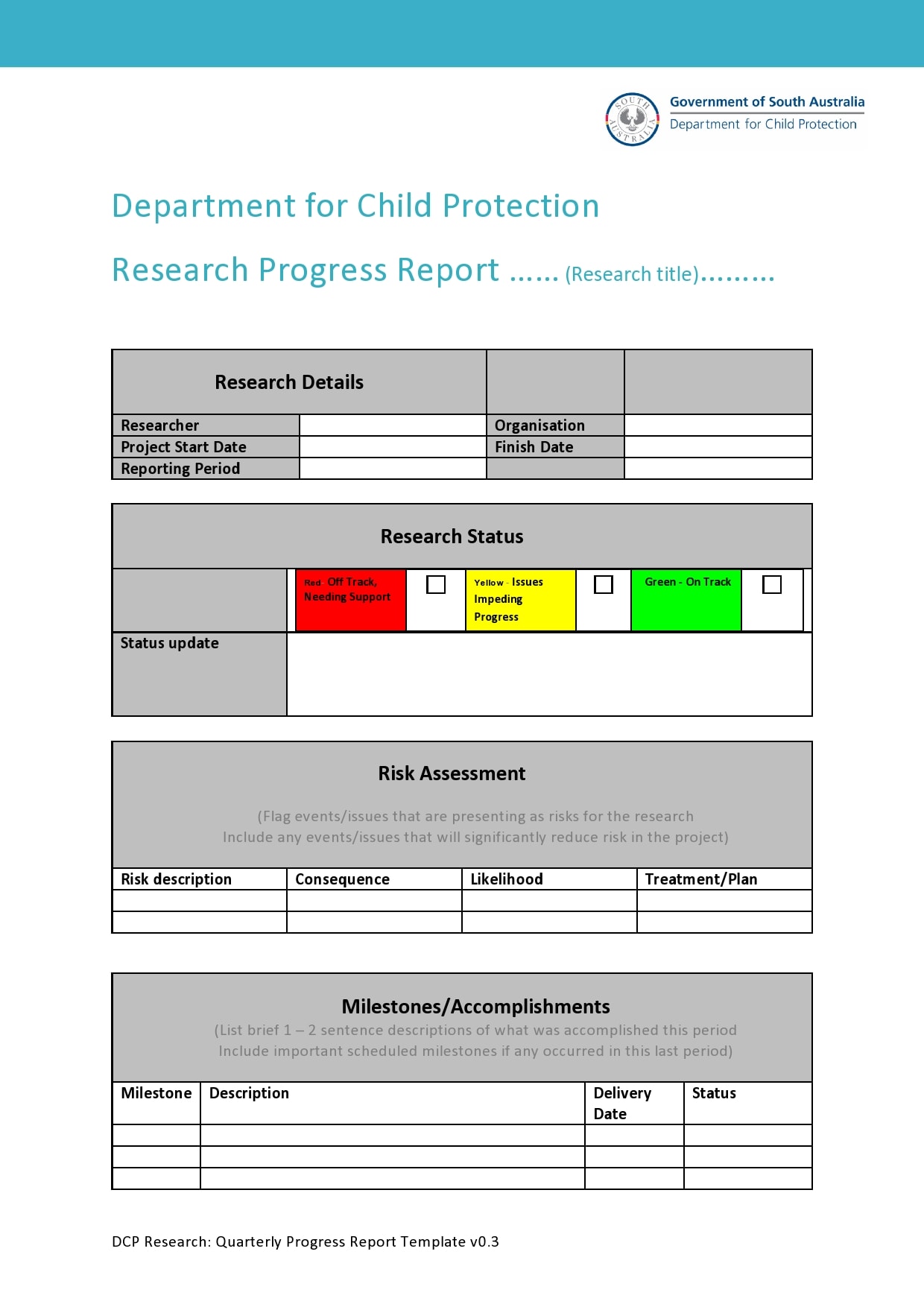

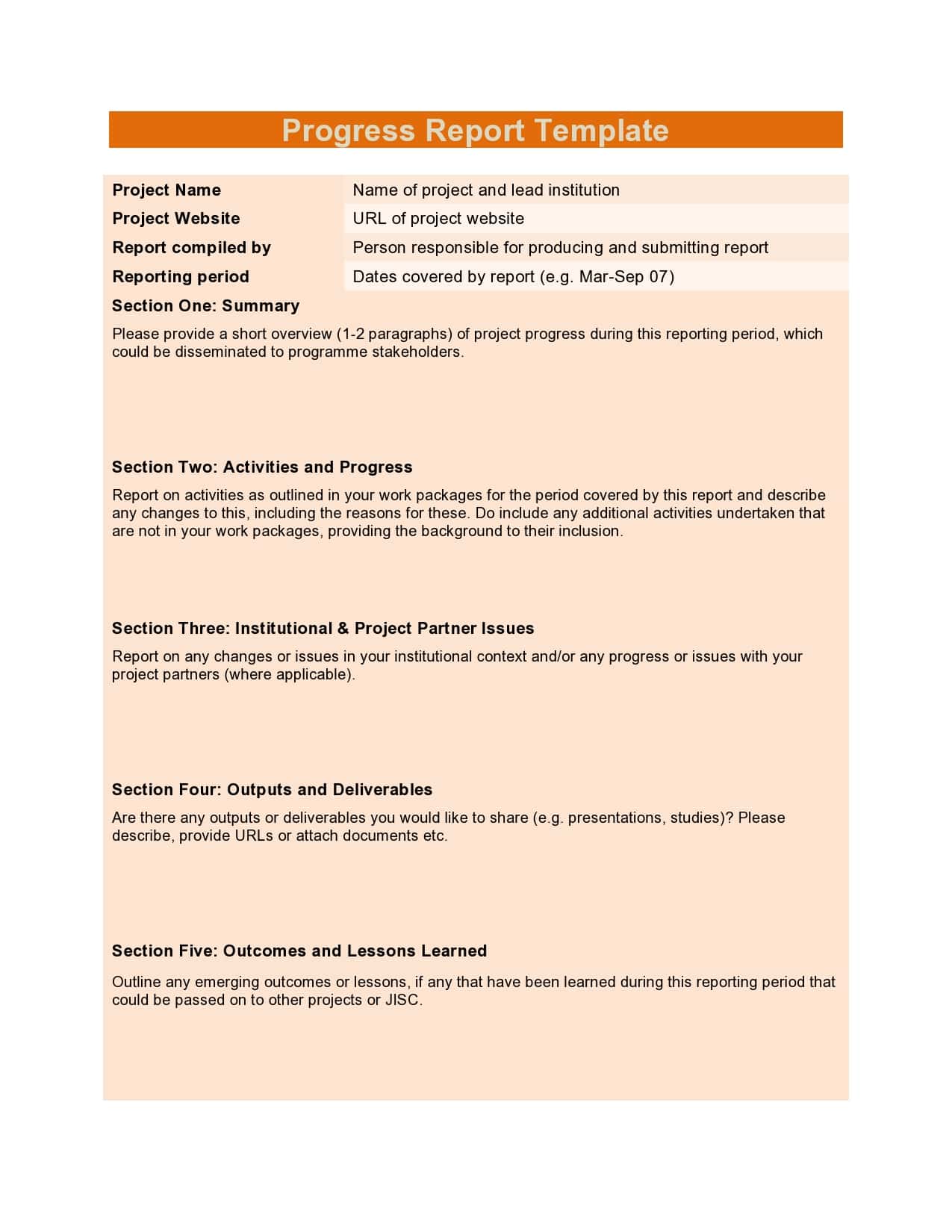

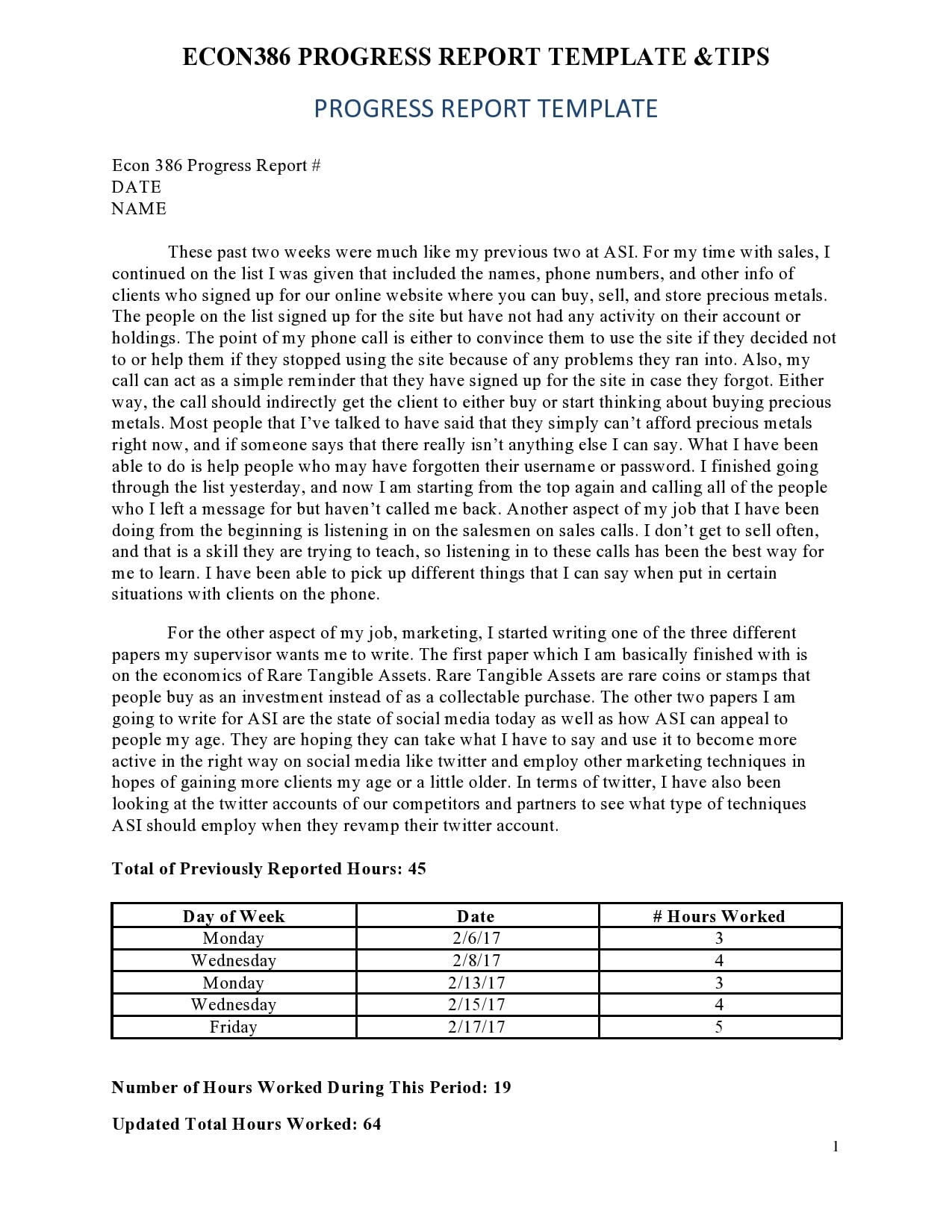
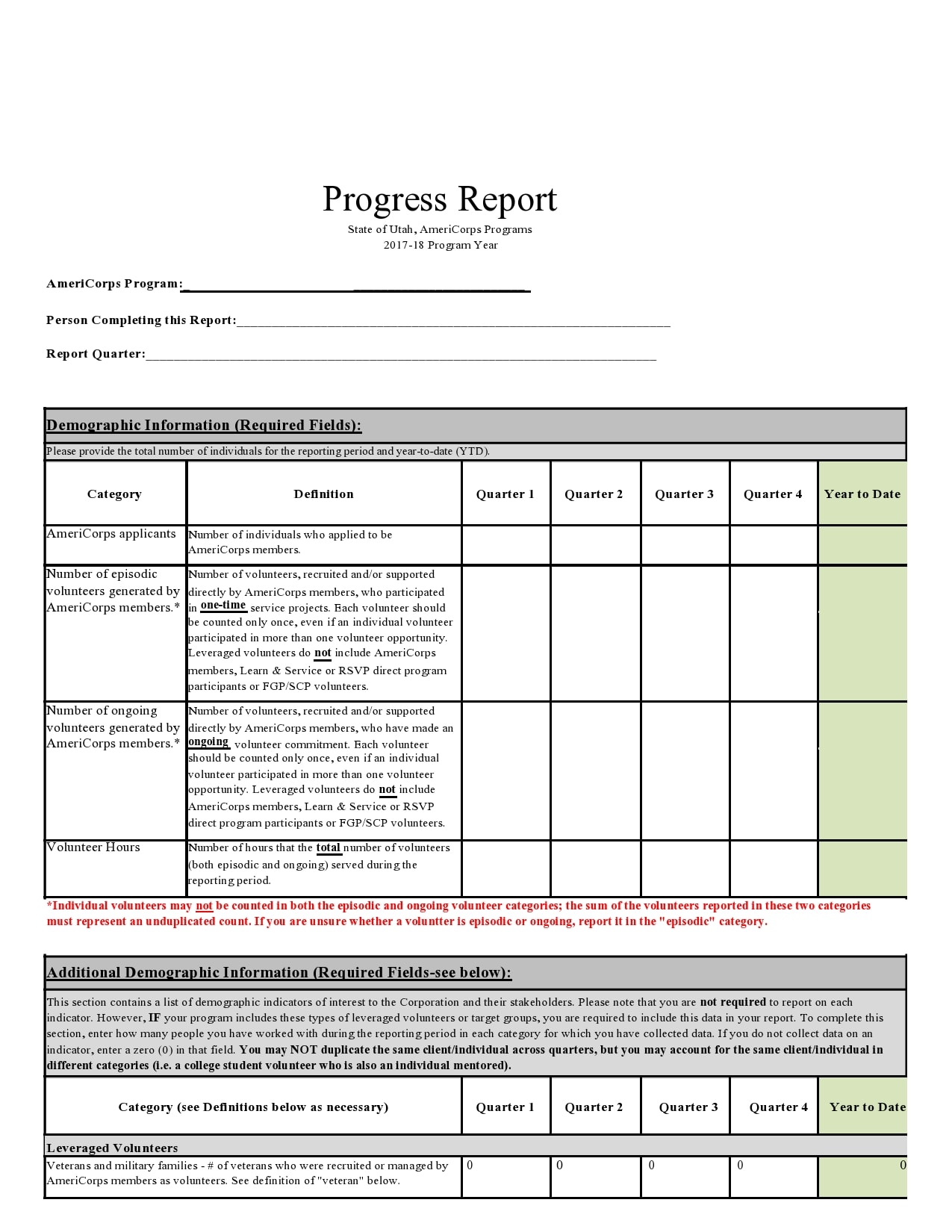
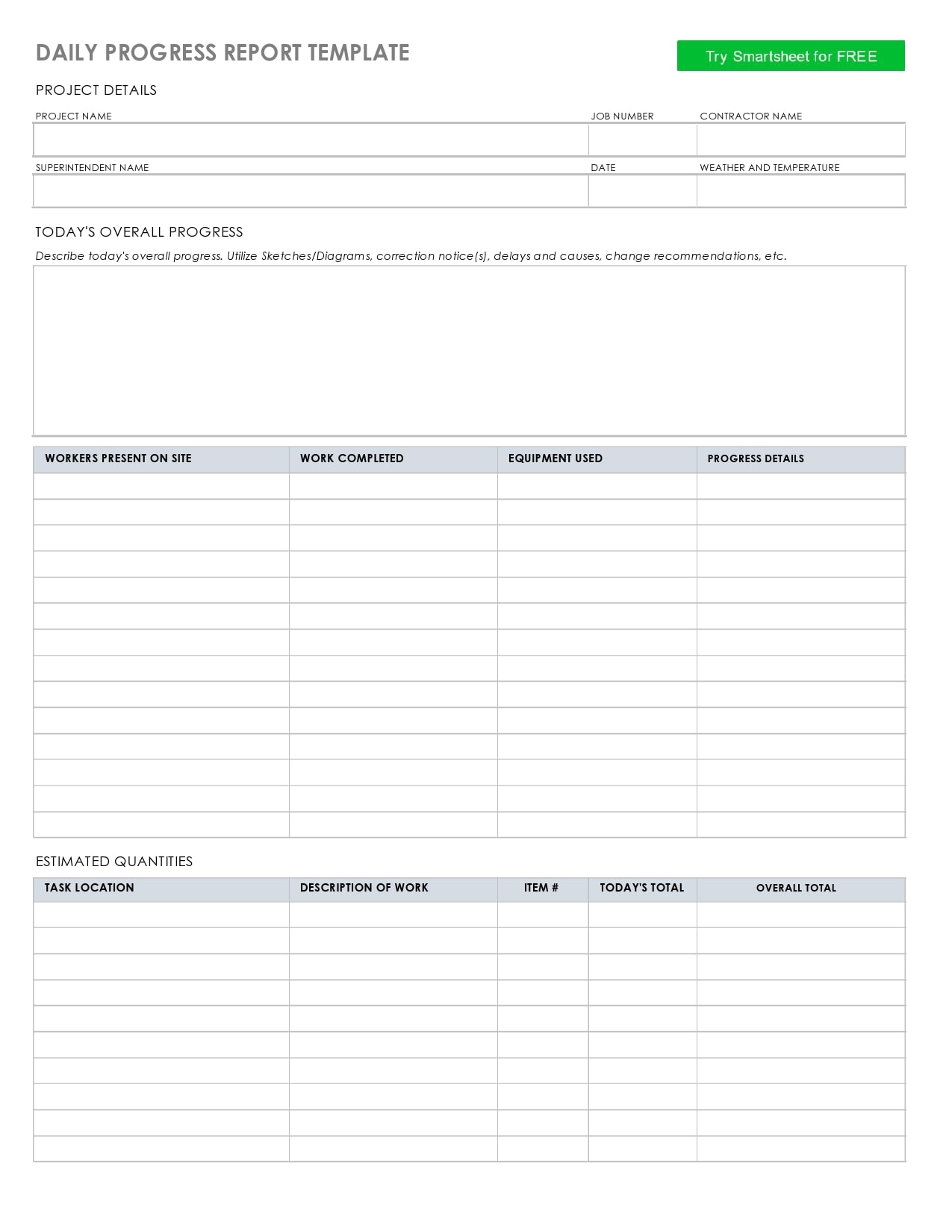
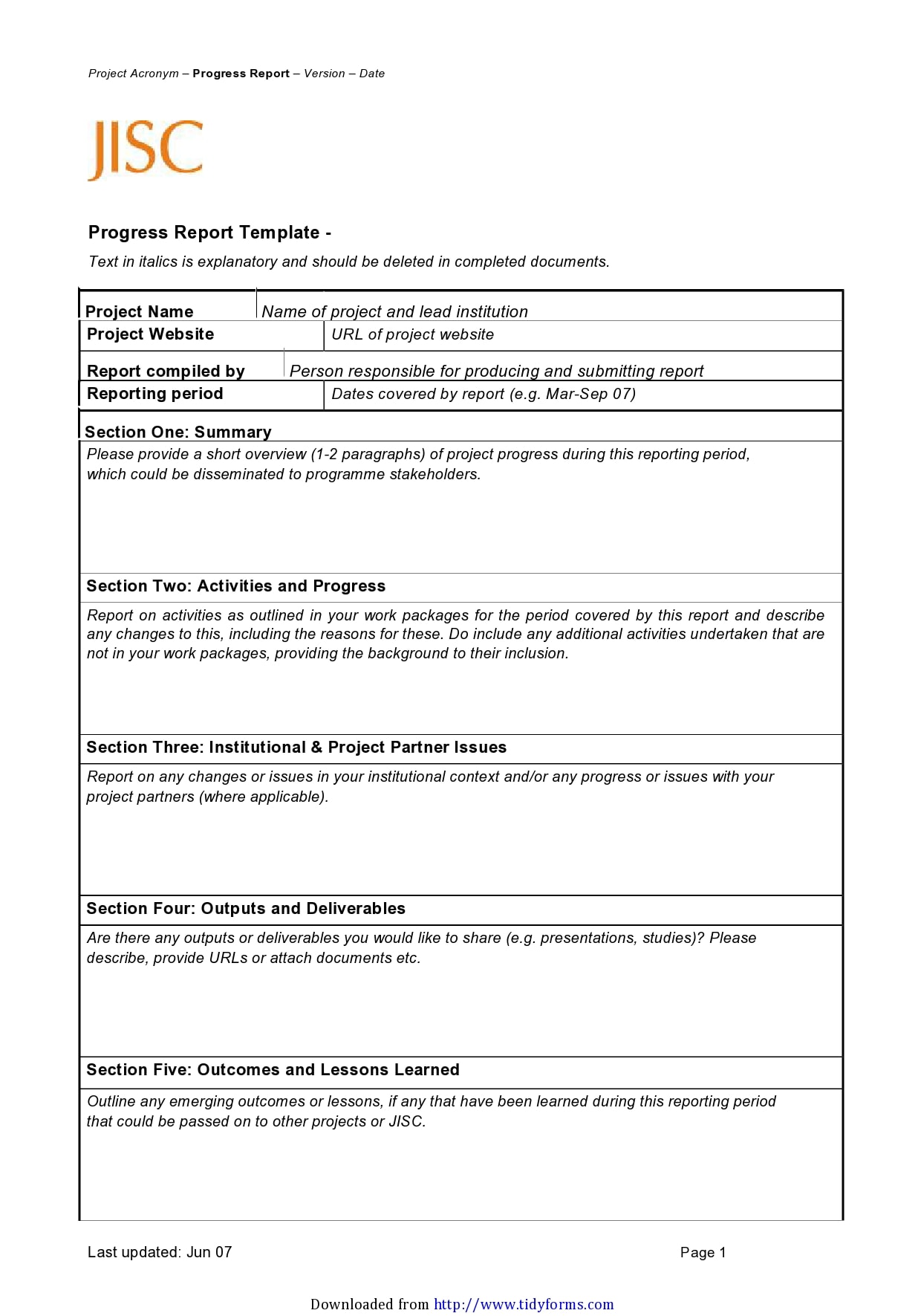

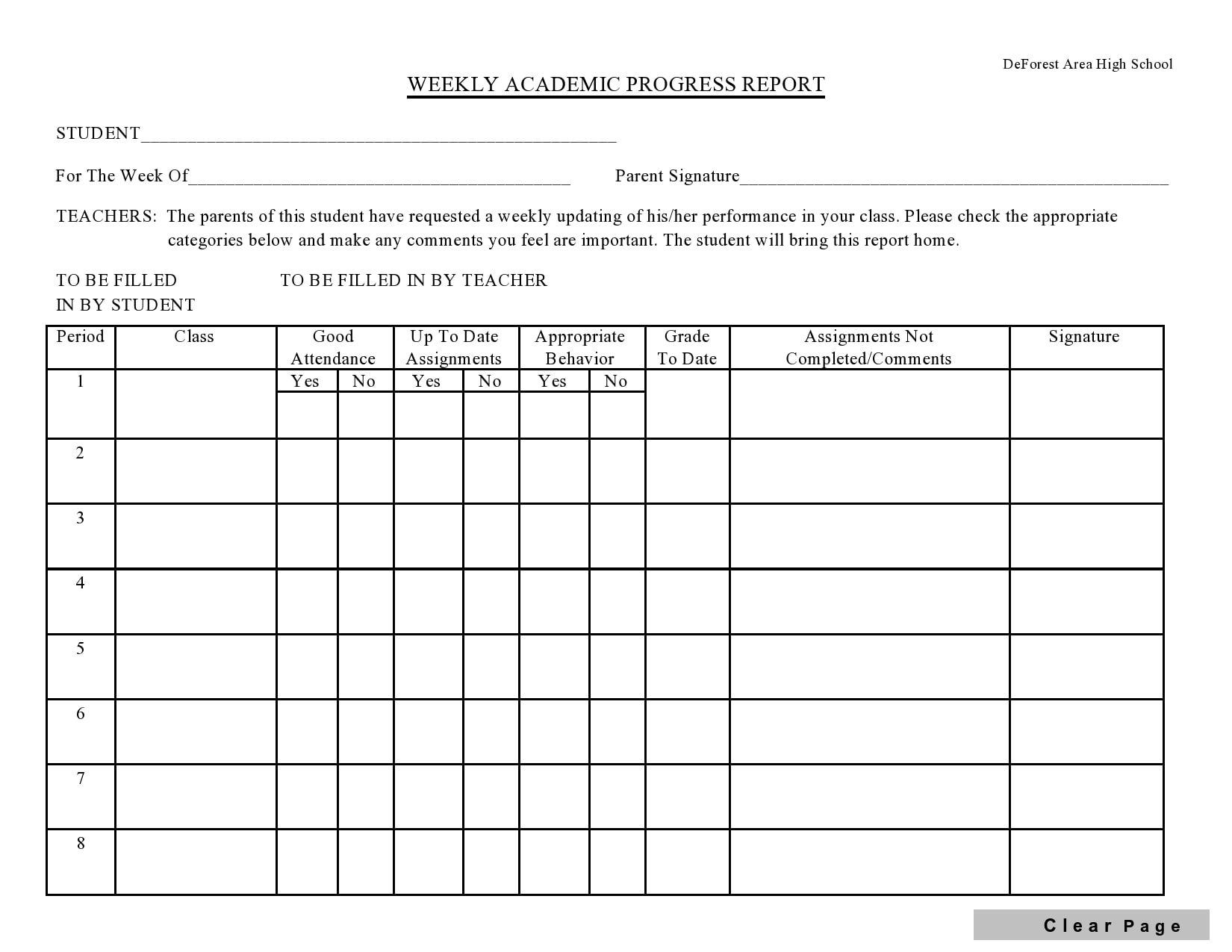
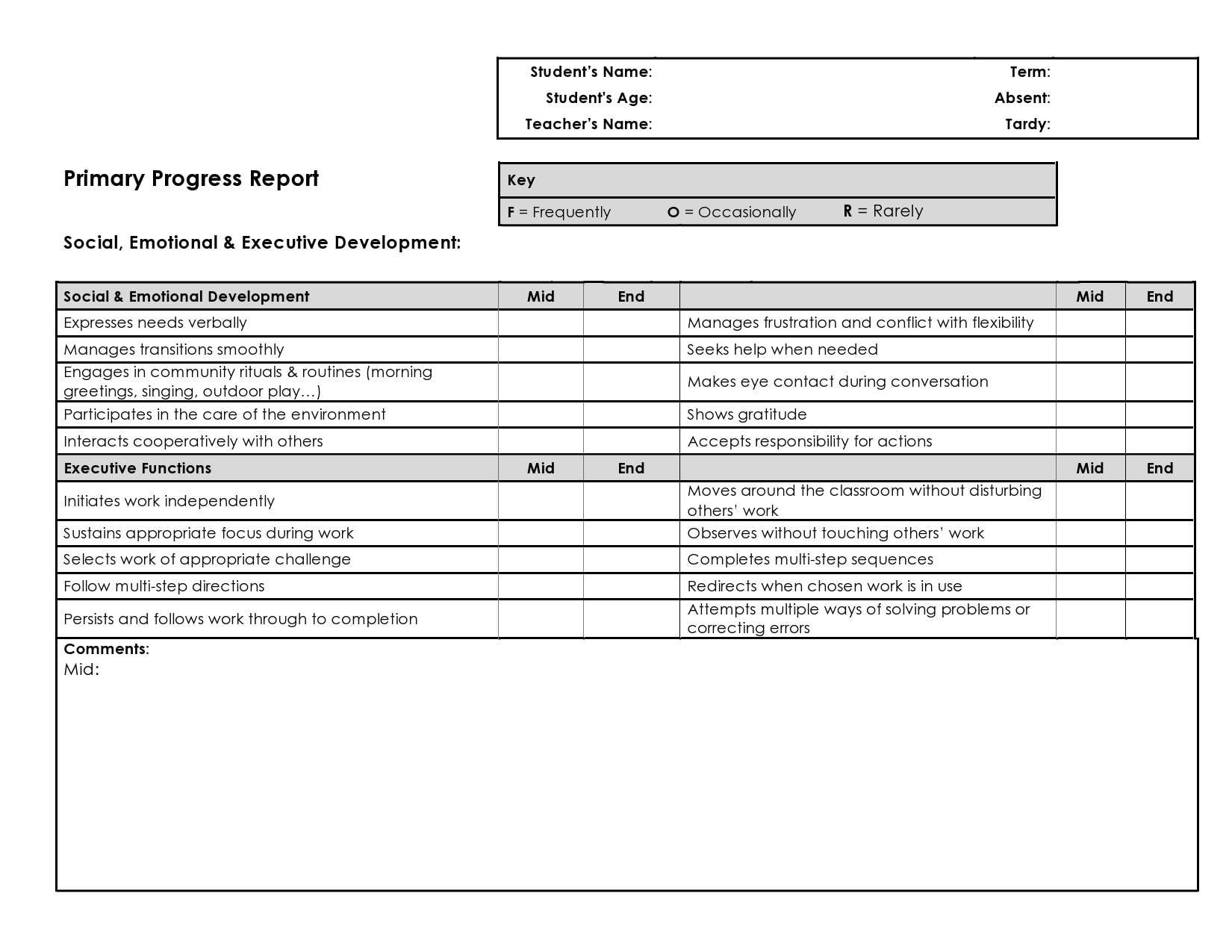

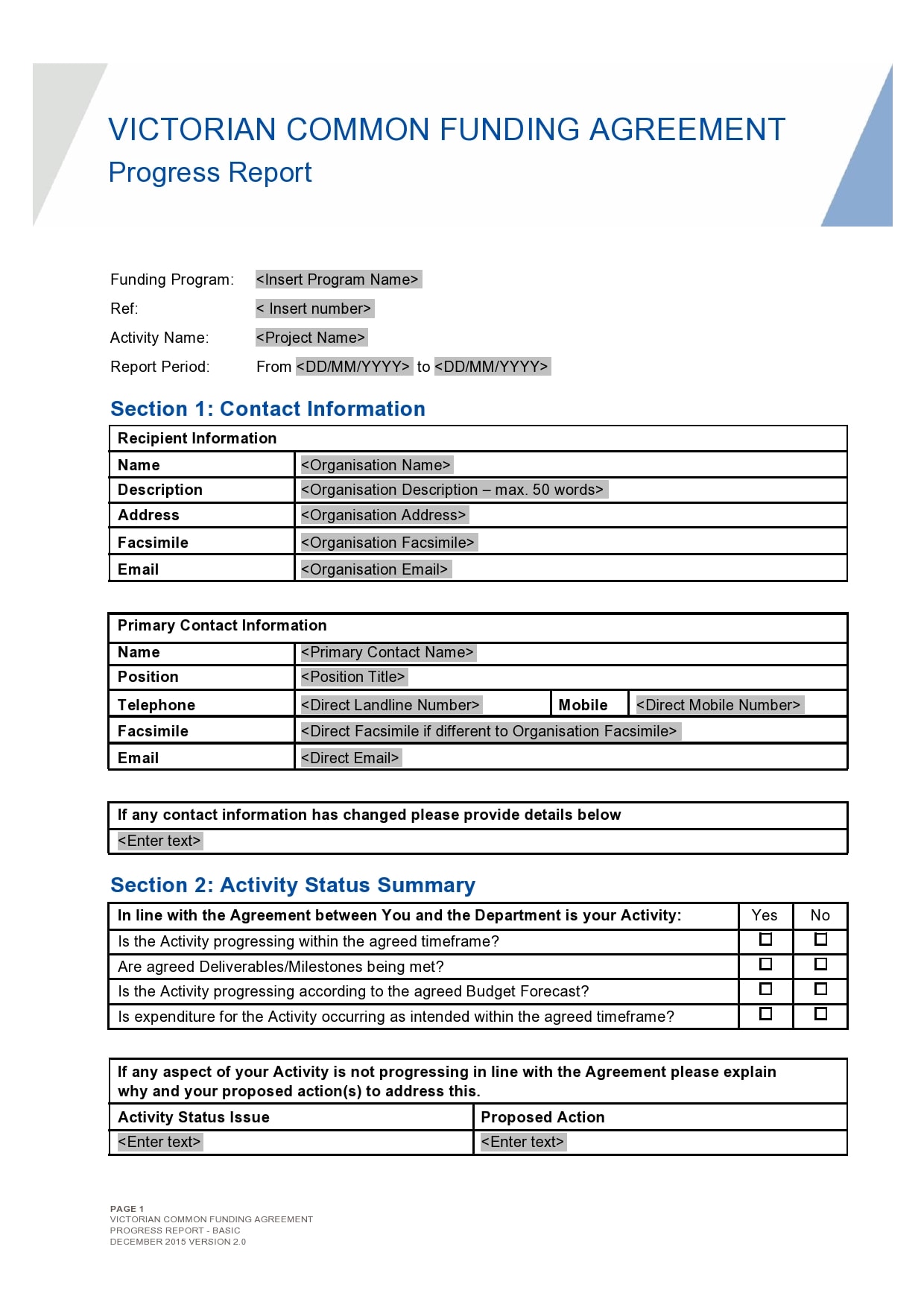

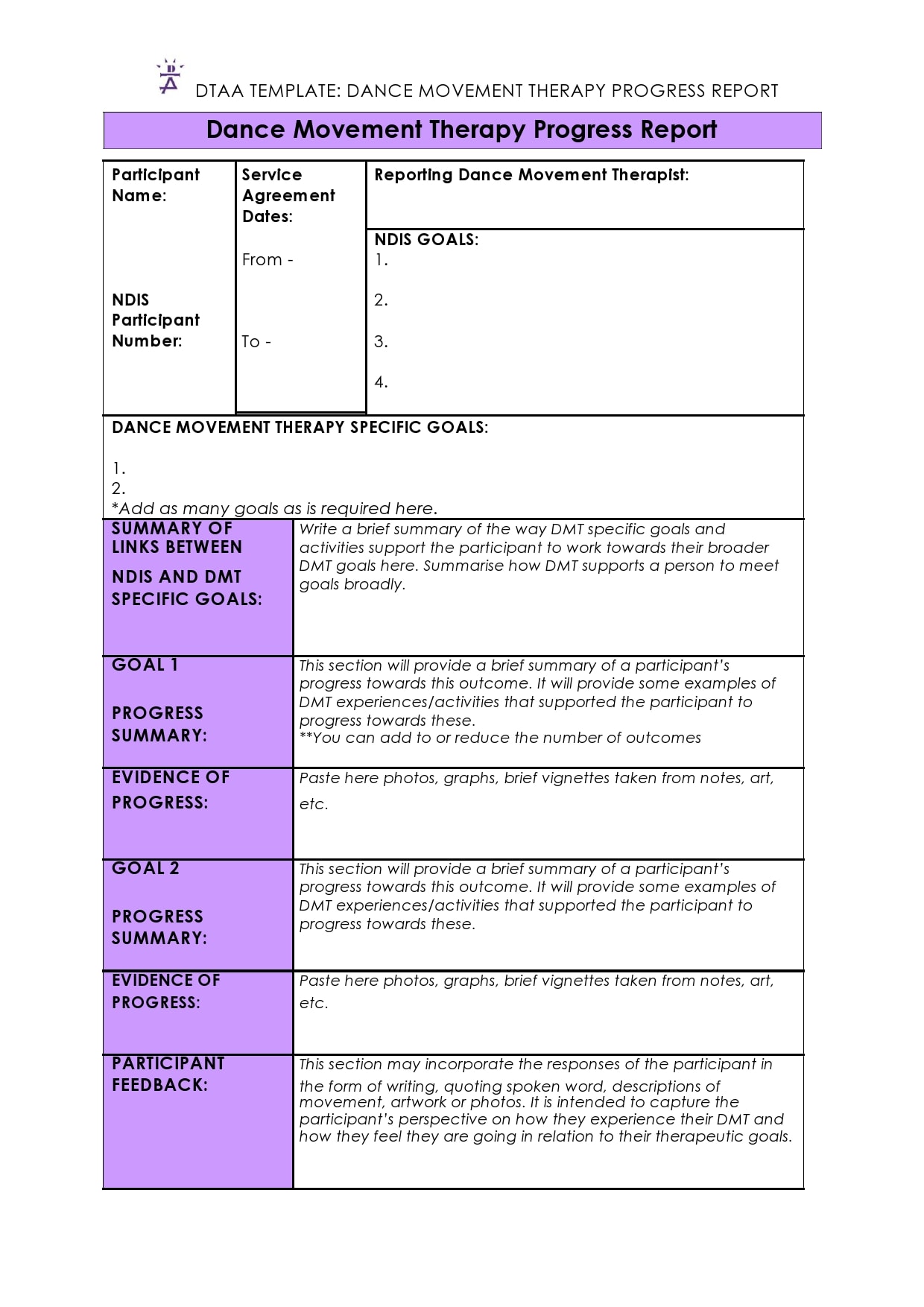
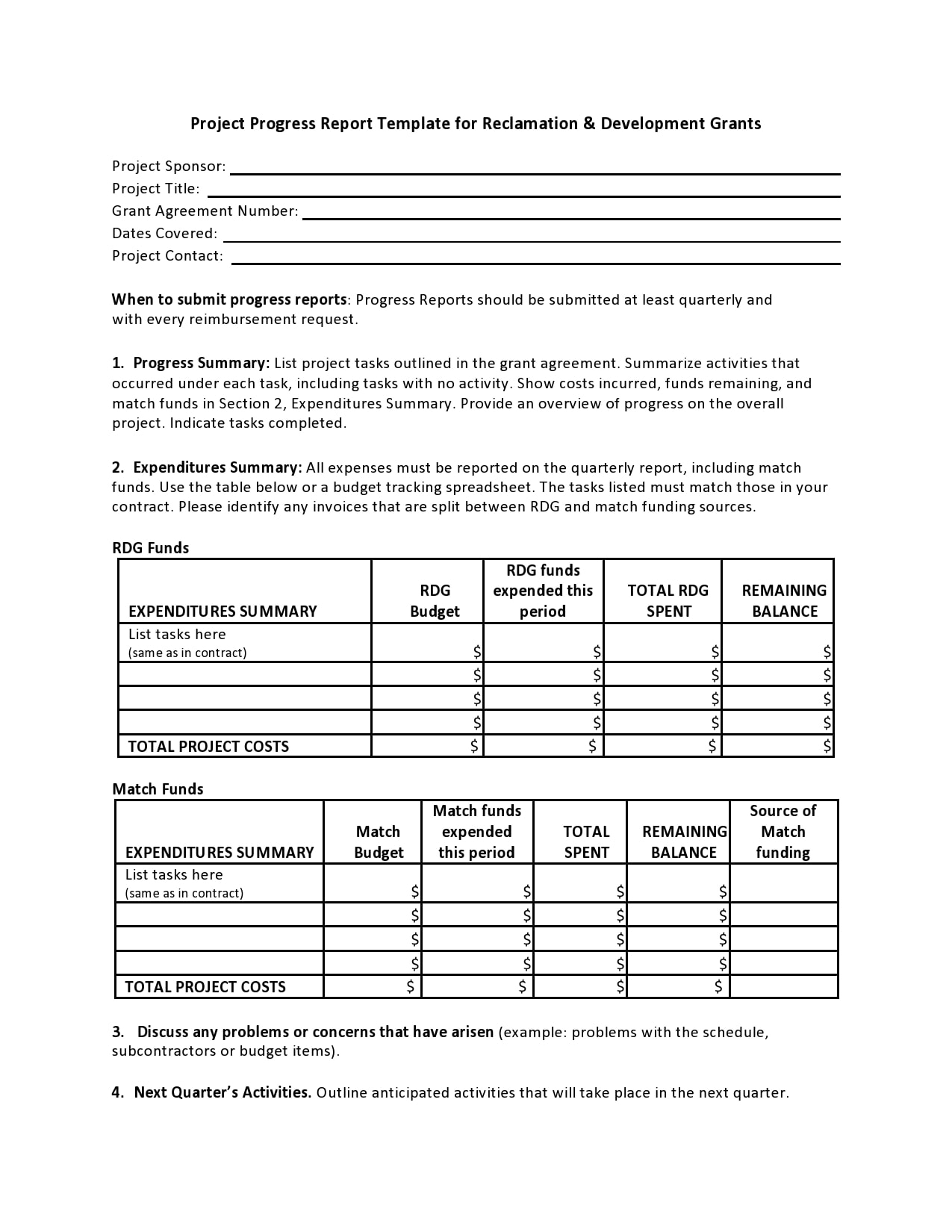



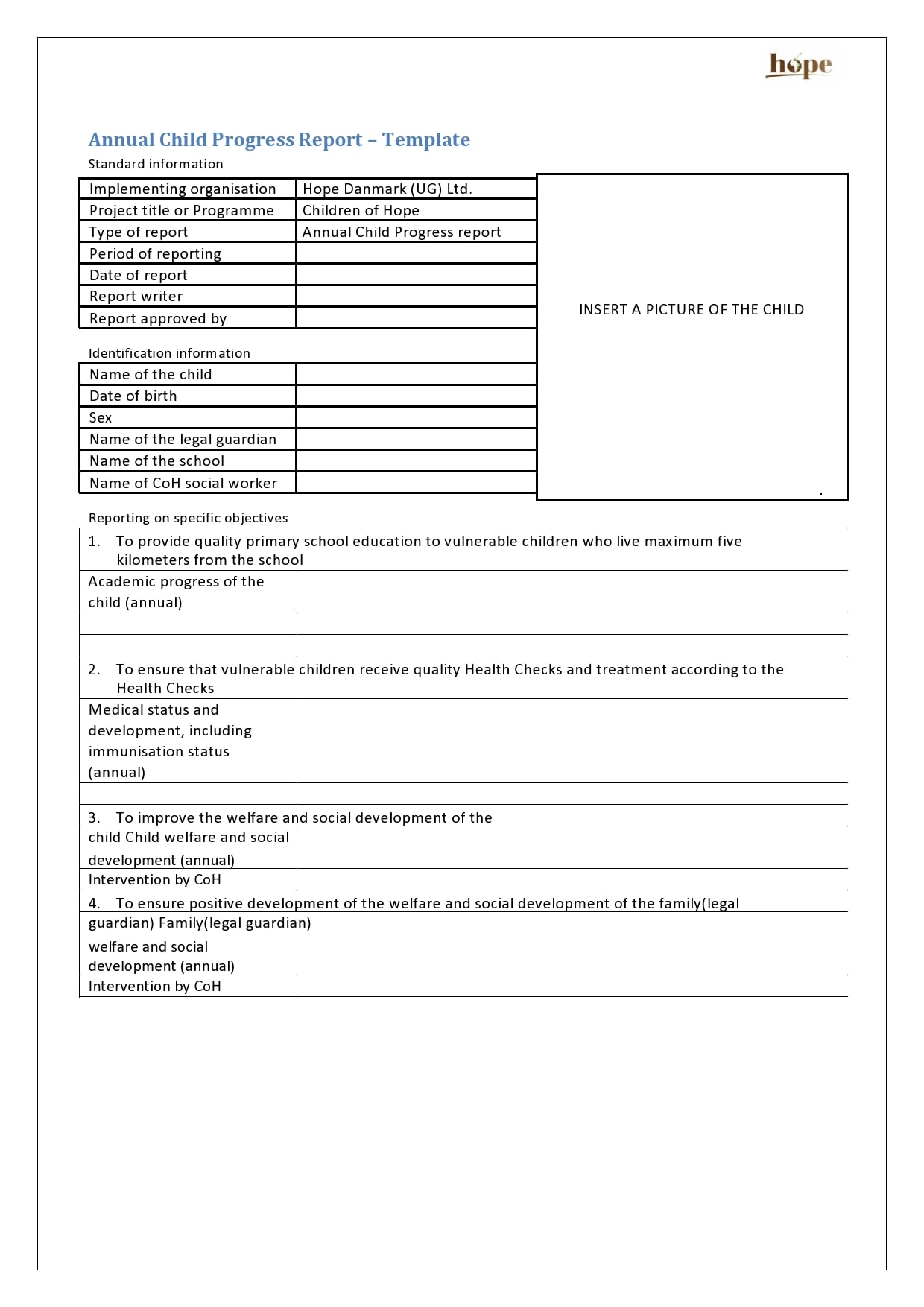
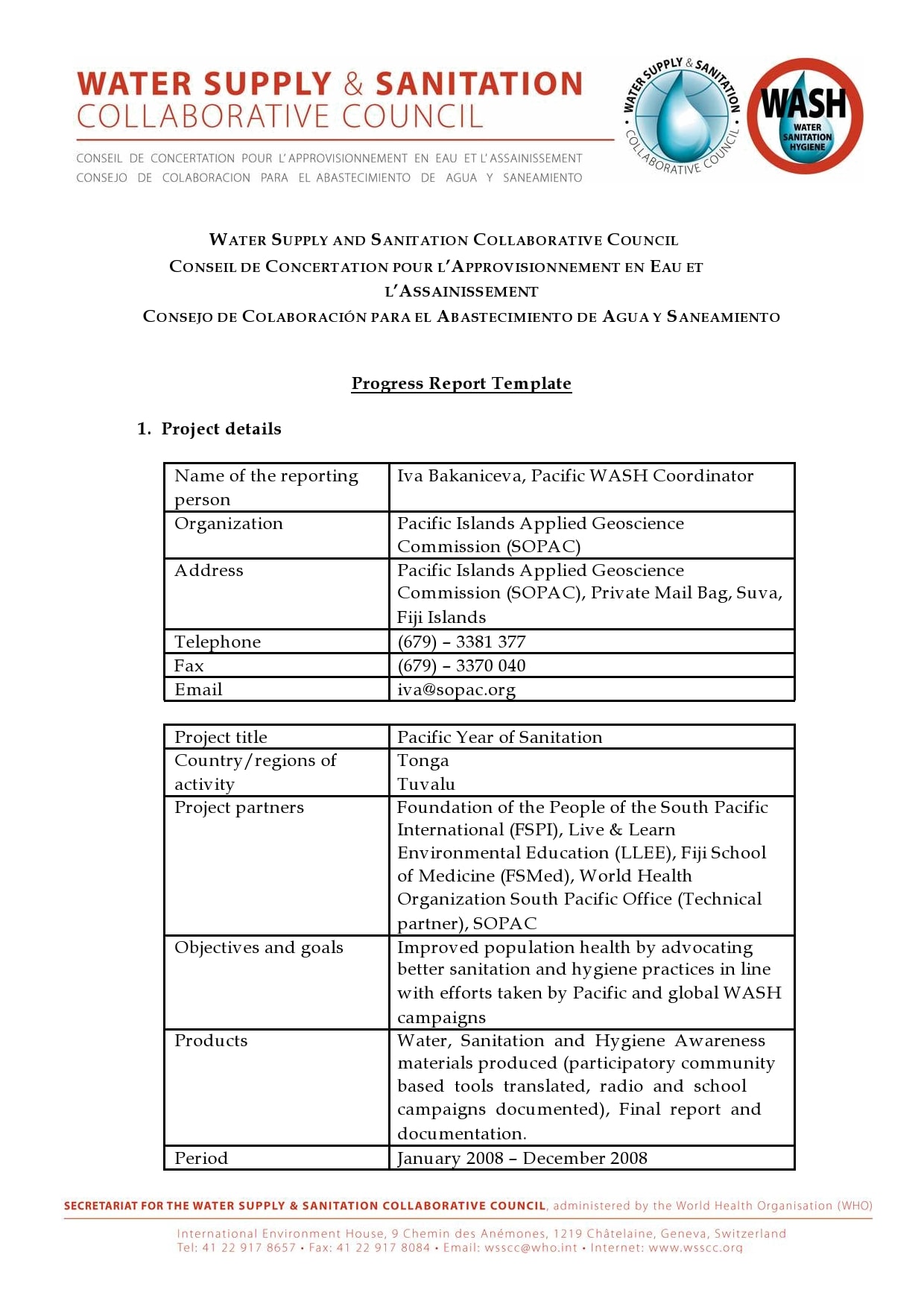
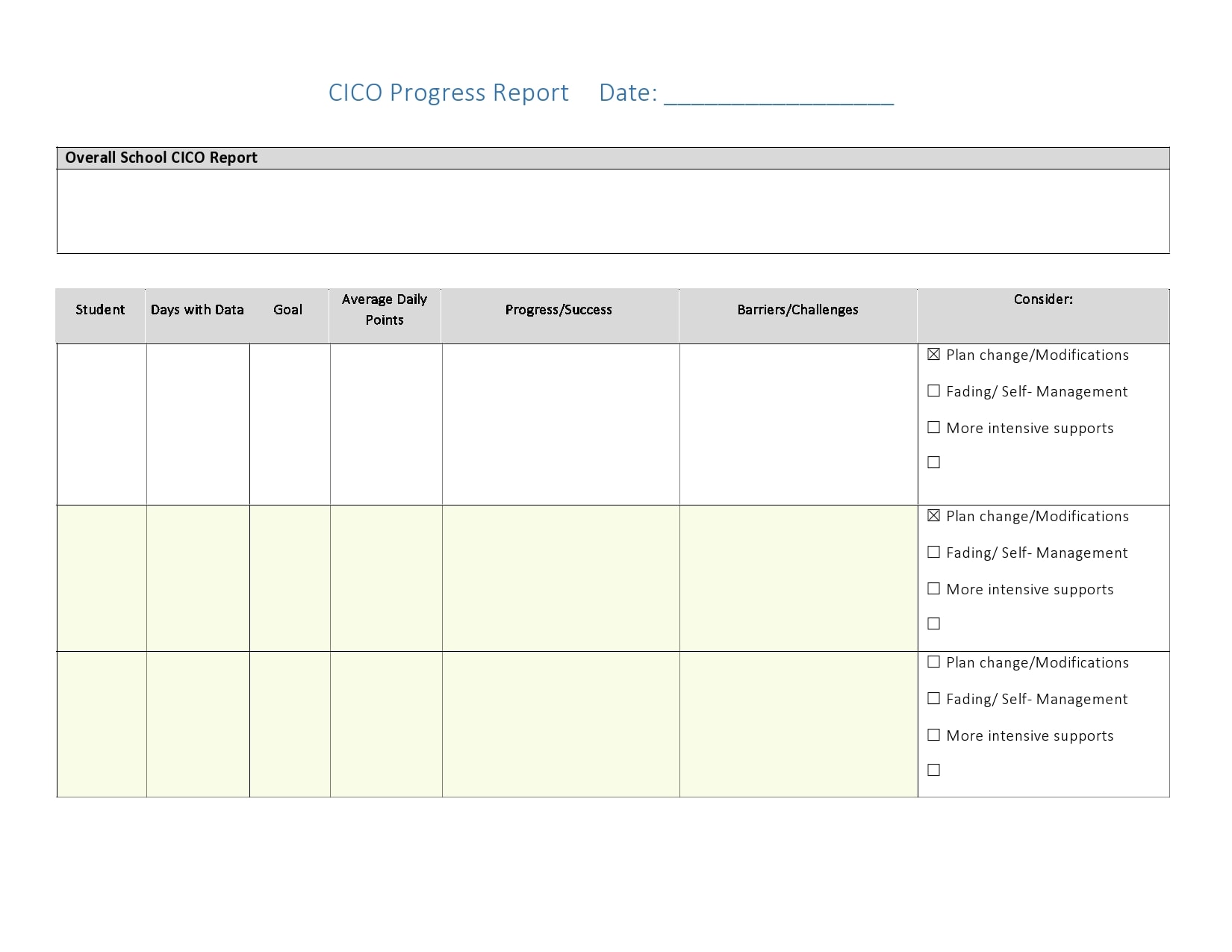
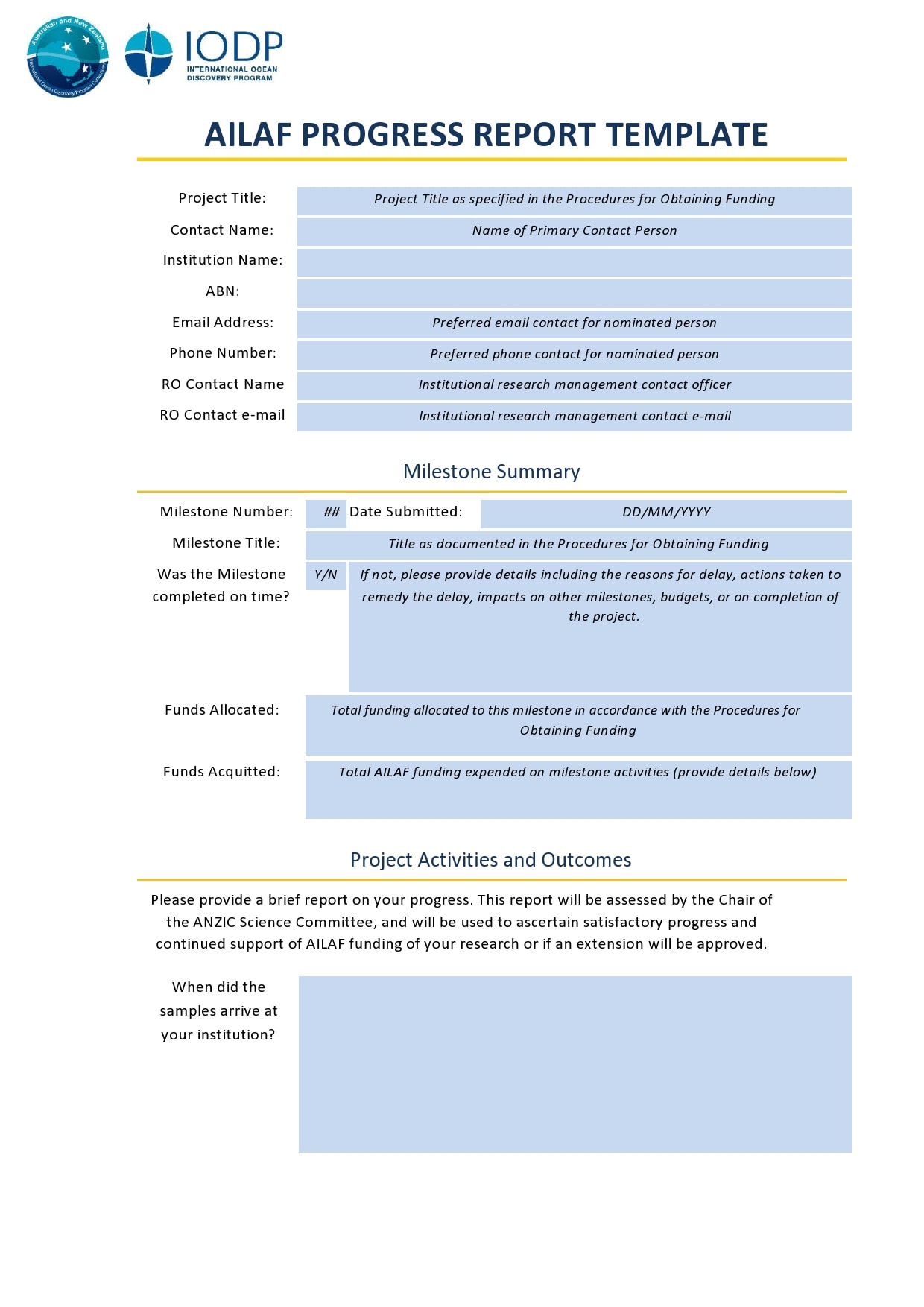



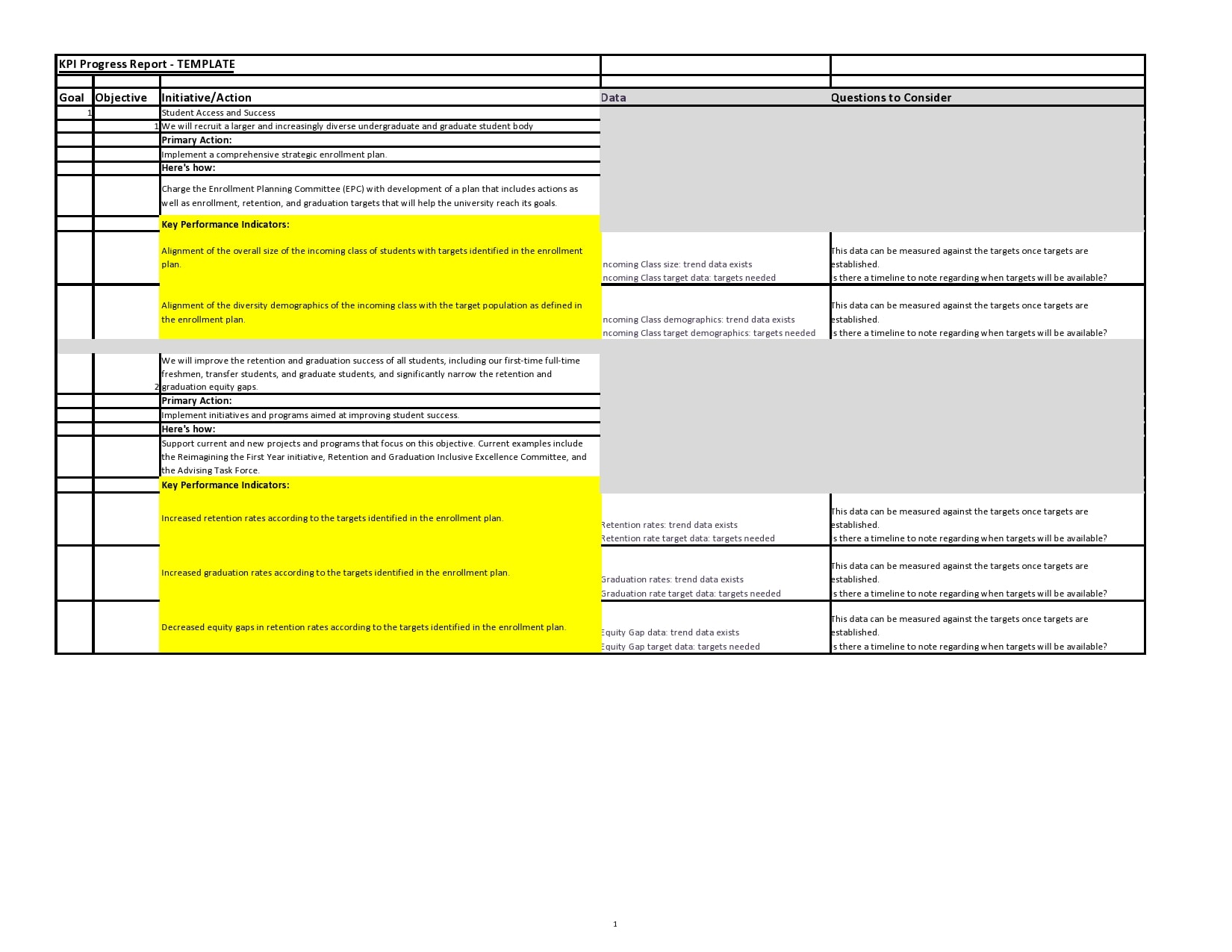


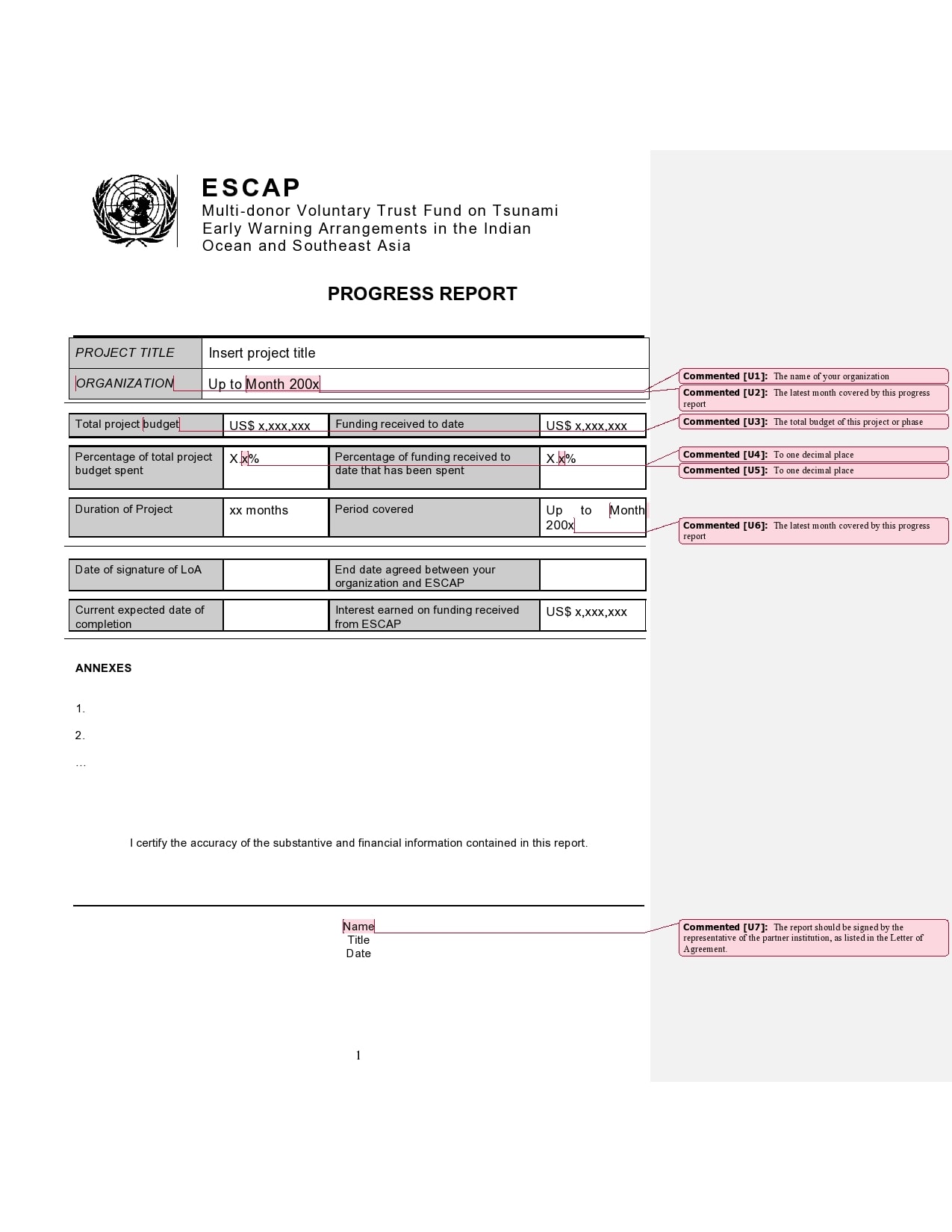


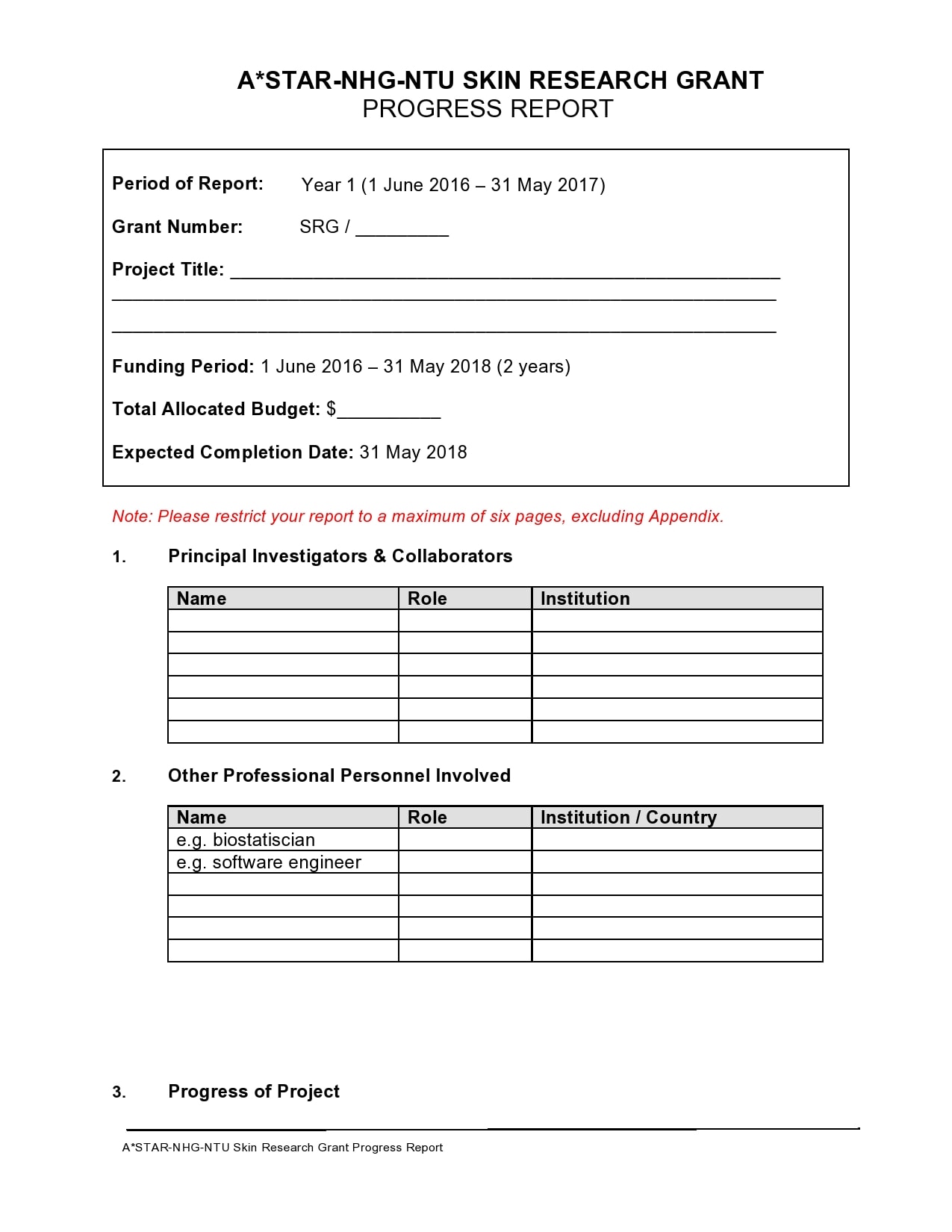
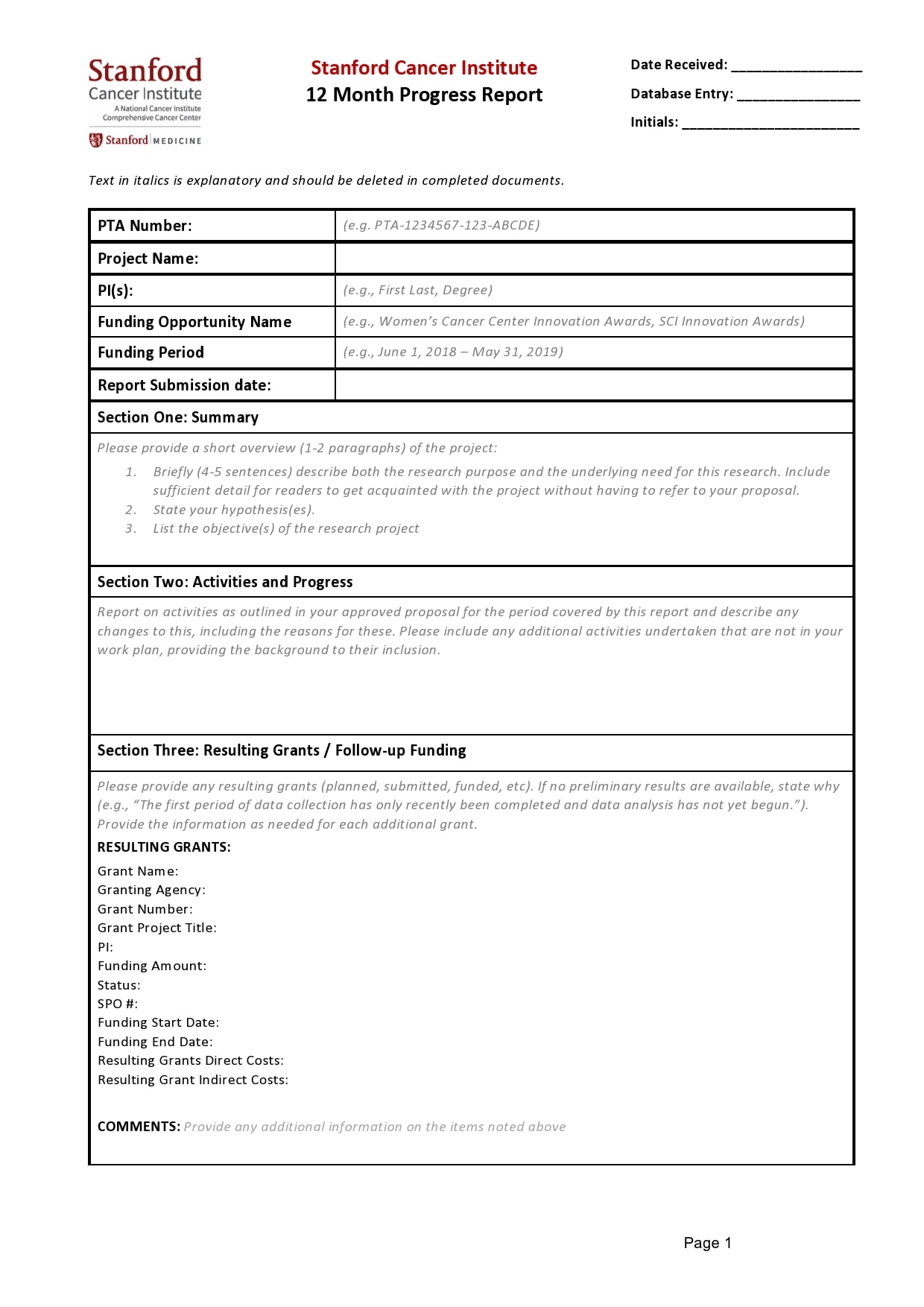
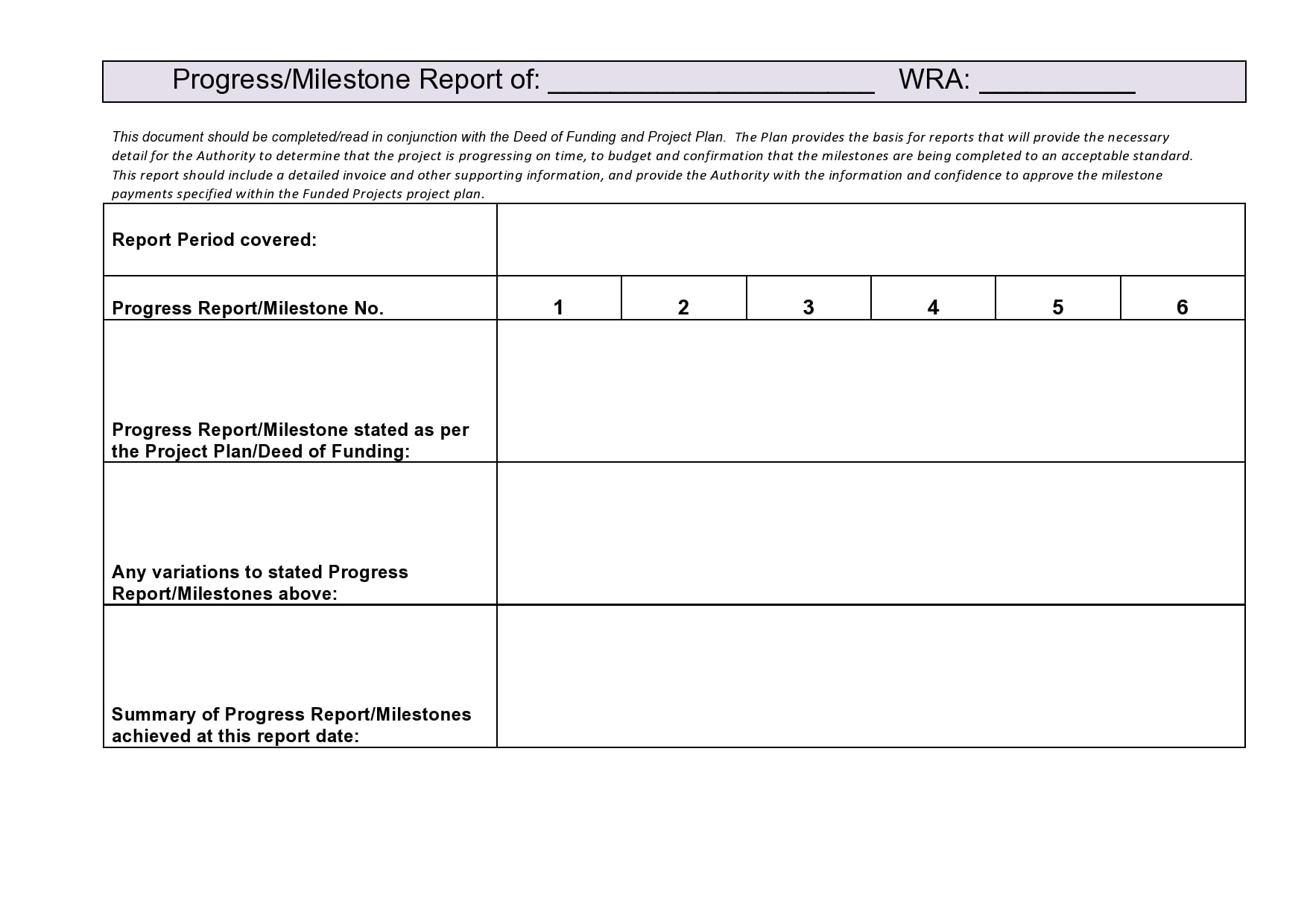
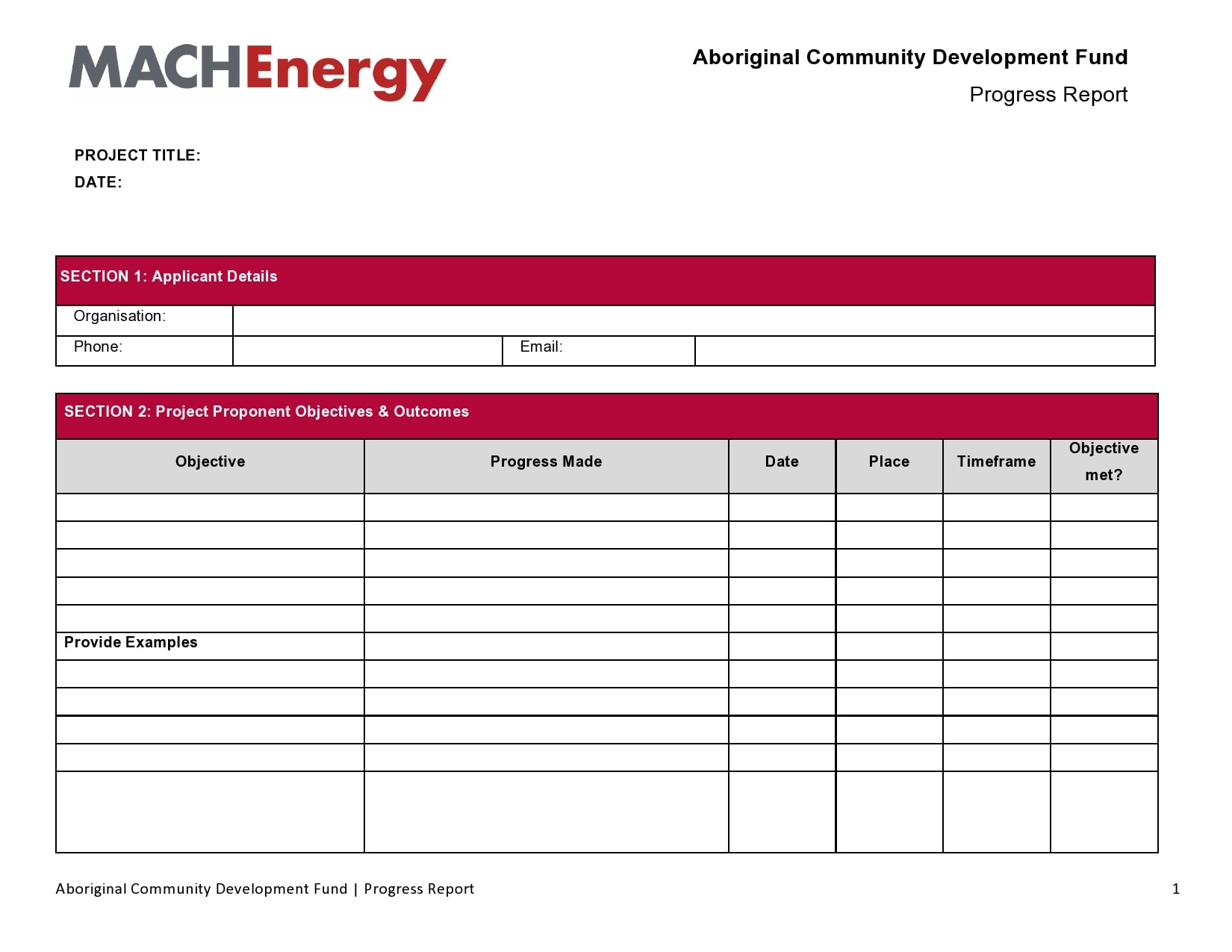
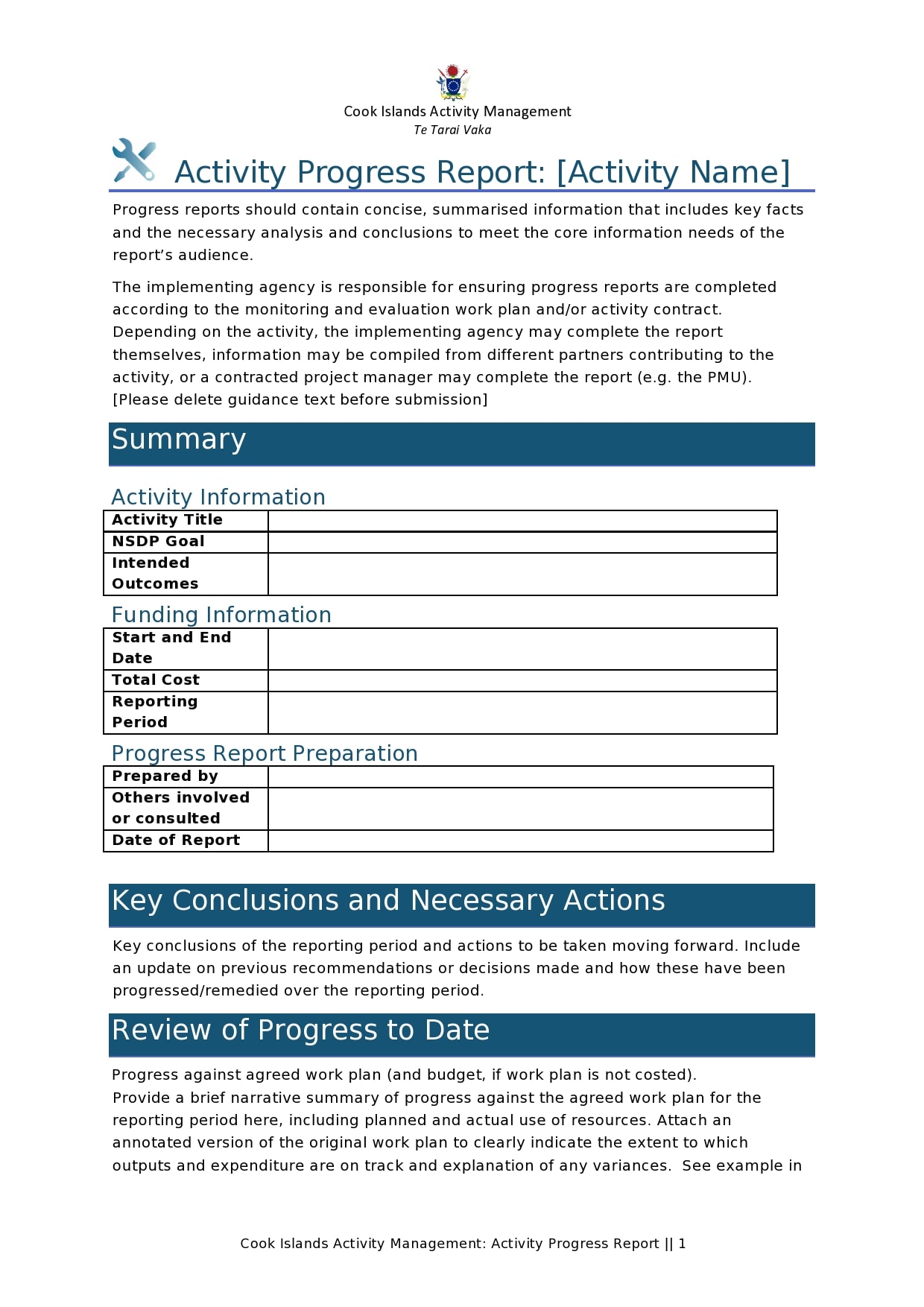
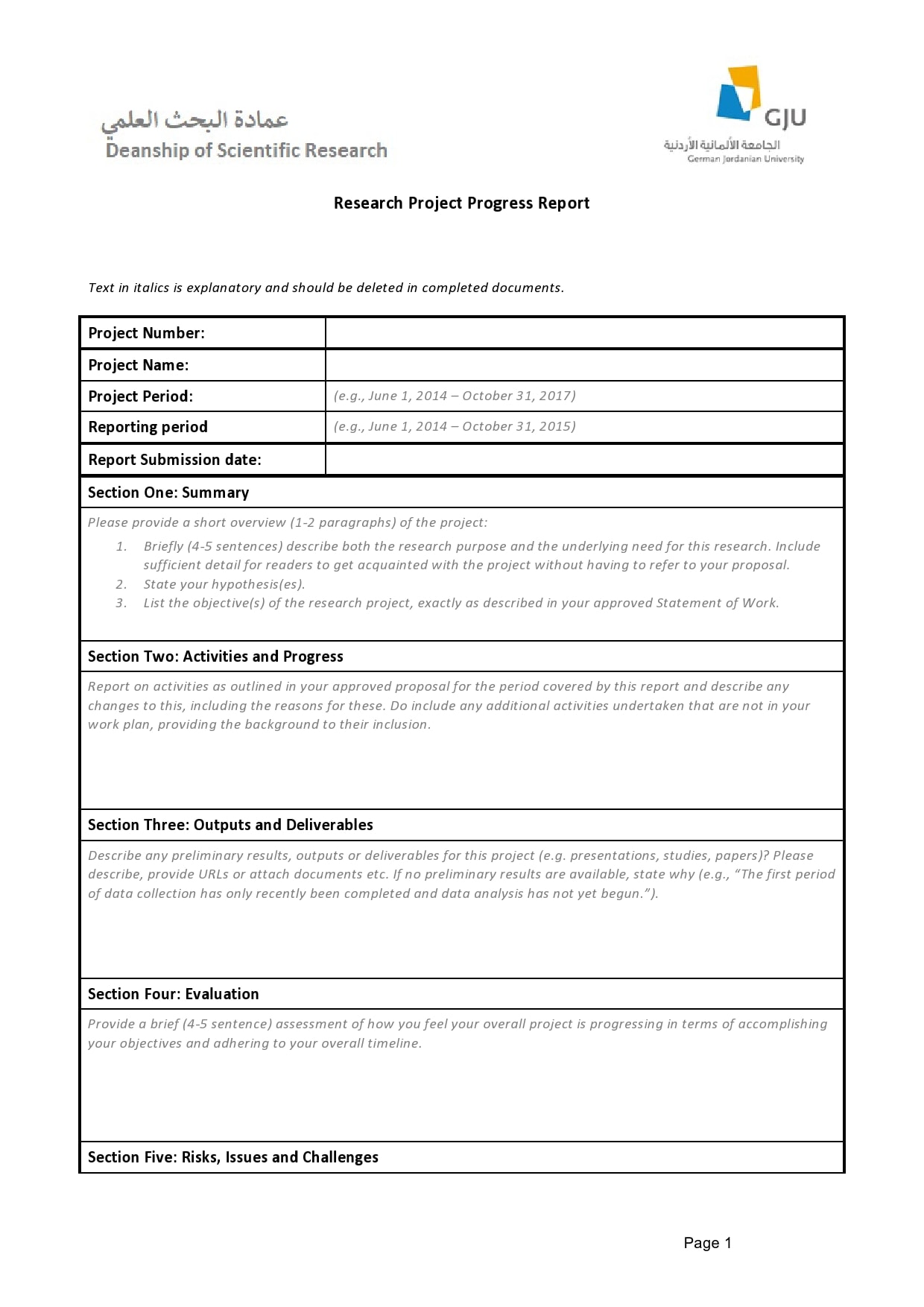





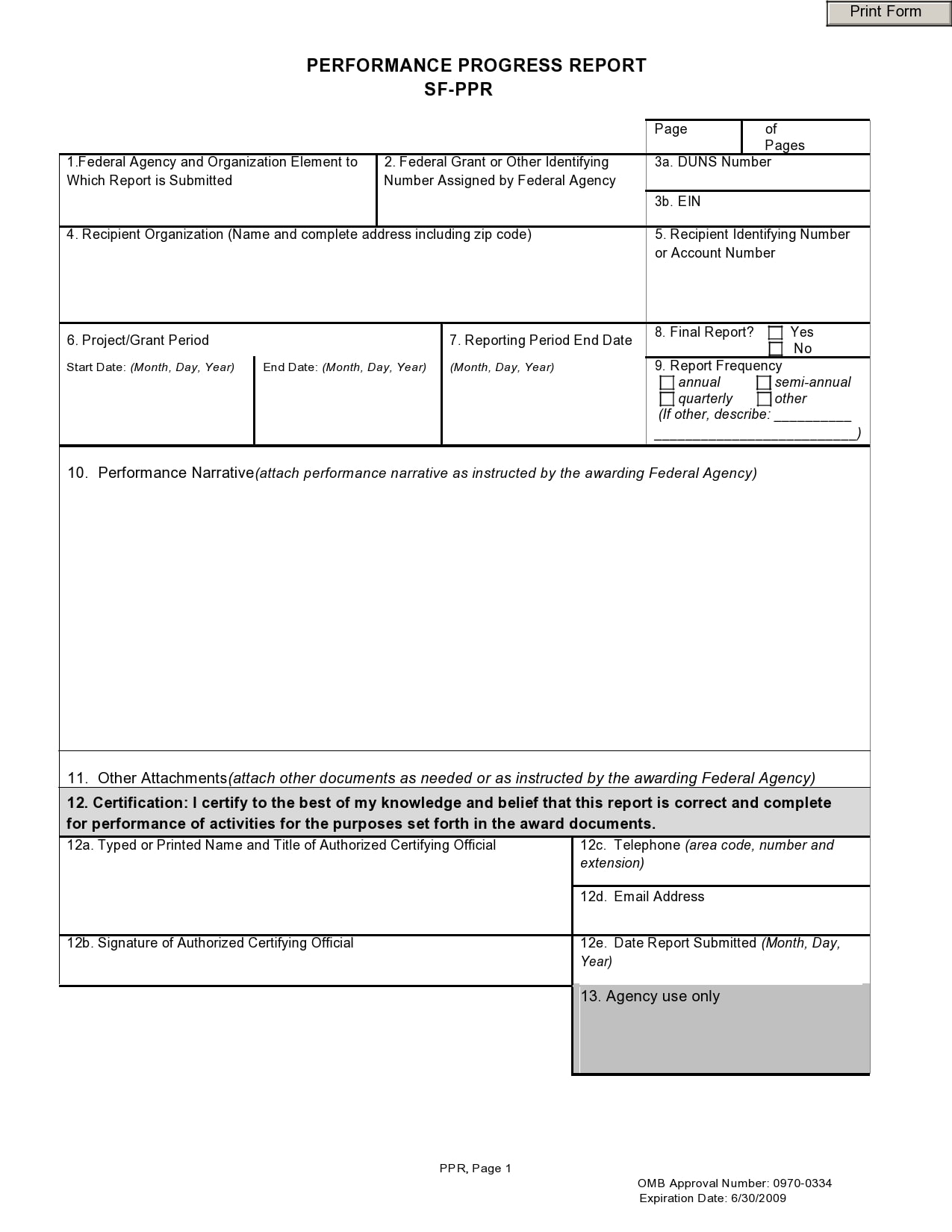
Tips for Successful Progress Reporting
To ensure that your progress reports are effective and well-received, consider the following tips:
1. Be Consistent
Establish a regular reporting schedule and stick to it. Consistency helps stakeholders anticipate updates and provides a sense of stability.
2. Keep it Concise
Avoid overwhelming stakeholders with too much information. Focus on the key highlights and provide enough context to ensure understanding without unnecessary details.
3. Use Visuals
Incorporate visual elements such as charts, graphs, or progress bars to make the report more visually appealing and easier to grasp at a glance.
4. Be Transparent
Don’t shy away from sharing challenges or potential issues. Transparency builds trust and allows stakeholders to provide support or suggest solutions.
5. Provide Next Steps
Include a section that outlines the next steps and upcoming milestones. This helps stakeholders understand the project’s trajectory and what to expect in the future.
6. Seek Feedback
Encourage stakeholders to provide feedback on the progress report. This feedback can help improve future reports and ensure that they meet the needs of all stakeholders.
Conclusion
A progress report is a powerful tool for project managers to communicate the current status of a project, detail completed and in-progress tasks, and address potential issues. By providing stakeholders with this information, project managers can keep everyone informed, evaluate the project’s progress, and make informed decisions about the next steps.
By following best practices and incorporating key elements into your progress report, you can ensure that your reports are effective, informative, and valuable to all stakeholders involved.
Progress Report Template – Download