Income statements are a crucial financial document that provides insights into a company’s financial performance over a specific period. They offer a snapshot of a company’s financial health by detailing its revenues, expenses, and resulting net profit or loss.
Understanding income statements is essential for various stakeholders, including management, investors, lenders, regulators, and analysts.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of income statements, their significance in business, the key users of income statements, the process of creating an income statement, and how to effectively interpret the information presented in an income statement.
What Is an Income Statement?
An income statement, also known as a profit and loss statement, is a financial document that summarizes a company’s revenues, expenses, and profits or losses over a specific period, typically quarterly or annually.
The primary purpose of an income statement is to provide stakeholders with a clear understanding of a company’s financial performance by showcasing how revenues are transformed into net income. By analyzing an income statement, stakeholders can make informed decisions, evaluate profitability, and assess the financial health of the company.
The Importance of the Income Statement in Business
Income statements are essential for businesses for several reasons.
Financial Performance Evaluation
Income statements help stakeholders evaluate a company’s financial performance by comparing revenues to expenses and determining the resulting profit or loss. By analyzing trends in revenues and expenses over time, stakeholders can identify areas of strength and weakness in a company’s operations. This information is crucial for making informed decisions about resource allocation, cost management, and revenue generation strategies.
Decision-Making
Management uses income statements to make strategic decisions about the company’s operations, investments, and growth opportunities. By analyzing the data presented in an income statement, management can identify areas of inefficiency, set performance targets, and allocate resources effectively. Income statements provide a clear picture of a company’s financial health, helping management make informed decisions that drive business success.
Investor and Lender Analysis
Investors and lenders rely on income statements to assess a company’s profitability, sustainability, and financial health before making investment or lending decisions. By reviewing key financial metrics such as net income, gross profit margin, and operating income, investors can evaluate the company’s ability to generate returns. Lenders use income statements to assess the company’s ability to repay debts and manage financial obligations effectively.
Performance Comparison
Income statements allow for comparing a company’s financial performance against competitors in the industry or previous periods to identify trends and areas for improvement. By benchmarking key financial metrics against industry standards or historical data, stakeholders can assess the company’s competitive position and performance trajectory. This information is valuable for setting strategic goals, evaluating performance targets, and identifying opportunities for growth.
Who Uses an Income Statement?
Various stakeholders rely on income statements to gain insights into a company’s financial performance. Some of the key users of income statements include:
Management
Management uses income statements to assess the company’s financial performance, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions about resource allocation and strategic planning. By analyzing key financial metrics such as net income, operating income, and gross profit margin, management can gauge the company’s profitability and sustainability. Income statements provide valuable insights that help management set performance targets, evaluate operational efficiency, and drive business success.
Investors
Investors analyze income statements to assess a company’s profitability, growth potential, and financial health before making investment decisions. By reviewing key financial metrics such as earnings per share, return on equity, and gross profit margin, investors can evaluate the company’s ability to generate returns and create shareholder value. Income statements provide critical information that helps investors make informed decisions about buying, holding, or selling stocks.
Lenders
Lenders use income statements to evaluate a company’s ability to repay debts and manage financial obligations effectively. By reviewing key financial metrics such as cash flow, debt-to-equity ratio, and interest coverage ratio, lenders can assess the company’s creditworthiness and risk profile. Income statements provide lenders with valuable insights into the company’s financial health, liquidity position, and ability to meet debt obligations.
Regulators
Regulators use income statements to ensure compliance with financial reporting standards and regulations. By reviewing the accuracy and completeness of the information presented in an income statement, regulators can verify that the company is following accounting principles and disclosure requirements. Income statements play a crucial role in financial transparency and accountability, helping regulators monitor the integrity of financial reporting practices.
Analysts
Analysts compare income statements across companies and industries to evaluate performance, identify trends, and make investment recommendations. By conducting financial ratio analysis, trend analysis, and peer benchmarking, analysts can assess a company’s financial health and competitive position. Income statements provide analysts with critical information that helps them assess the company’s profitability, efficiency, and growth potential.
Components of an Income Statement
An income statement comprises several key components that provide valuable insights into a company’s financial performance. These components include:
– Revenues: The total income generated by the company from its core operations.
– Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): The direct costs associated with producing goods or services sold by the company.
– Gross Profit: The difference between revenues and the cost of goods sold.
– Operating Expenses: The costs incurred by the company to operate its business, such as salaries, rent, utilities, and marketing expenses.
– Operating Income: The profit generated from the company’s primary business activities before interest and taxes.
– Net Income: The final profit or loss after all expenses have been accounted for.
How to Create an Income Statement
Creating an income statement involves several steps to compile and organize financial data effectively. Here is a detailed guide on how to create an income statement:
Gather Financial Data
The first step in creating an income statement is to gather financial data for the specific period you want to report on. This includes information on revenues, expenses, cost of goods sold, and other financial transactions. Ensure that the data is accurate, complete, and up-to-date to provide a clear picture of the company’s financial performance.
Categorize Revenues and Expenses
Once you have gathered the financial data, categorize revenues and expenses into relevant categories to organize the information effectively. Common categories include operating revenues, non-operating revenues, operating expenses, and non-operating expenses. Categorizing revenues and expenses helps to simplify the income statement and make it easier to analyze.
Calculate Net Income
After categorizing revenues and expenses, calculate the net income by subtracting total expenses from total revenues. Net income is a key financial metric that reflects the company’s profitability for the specific period. It provides valuable insights into how well the company is performing in generating profits from its operations.
Prepare the Statement
Once you have calculated the net income, prepare the income statement by organizing the data into a formal format. Present revenues at the top, followed by cost of goods sold, gross profit, operating expenses, operating income, and net income. Use clear headings and subheadings to make the income statement easy to read and understand for stakeholders.
How to Read an Income Statement
Reading an income statement effectively requires understanding key components, financial metrics, and performance indicators. Here are some tips for interpreting an income statement:
Revenue Section
The revenue section of the income statement shows the total income generated by the company from its core operations. It includes sales revenue, service revenue, and any other sources of income. Analyzing the revenue section helps stakeholders gauge the company’s ability to generate income and assess the effectiveness of its sales and marketing efforts.
Expense Section
The expense section of the income statement lists all costs incurred by the company to generate revenue. It includes operating expenses, such as salaries, rent, utilities, and cost of goods sold. Analyzing the expense section helps stakeholders understand the company’s cost structure, efficiency of operations, and profitability margins.
Gross Profit Margin
The gross profit margin is calculated by subtracting the cost of goods sold from total revenue and dividing the result by total revenue. It reflects the profitability of a company’s core business operations and indicates how efficiently the company is producing goods or services. A higher gross profit margin suggests that the company is effectively managing production costs and generating profits from its core activities.
Operating Income
Operating income is derived by subtracting operating expenses from gross profit. It represents the profit generated from the company’s primary business activities before interest and taxes. Operating income is a key indicator of a company’s operational efficiency and profitability. By analyzing operating income, stakeholders can assess how well the company is managing costs and generating profits from its core operations.
Net Income
Net income is the final figure on the income statement, obtained by subtracting total expenses from total revenues. It represents the company’s overall profitability after all expenses have been accounted for. Net income is a critical financial metric that indicates the company’s bottom-line performance. A positive net income signifies profitability, while a negative net income indicates a loss.
Earnings Per Share (EPS)
Earnings per share are calculated by dividing the company’s net income by the number of outstanding shares. It indicates how much profit each share of stock generates for investors. EPS is a key metric used by investors to assess the company’s profitability and investment potential. A higher EPS suggests that the company is generating more profits per share, which may attract investors and drive stock prices up.
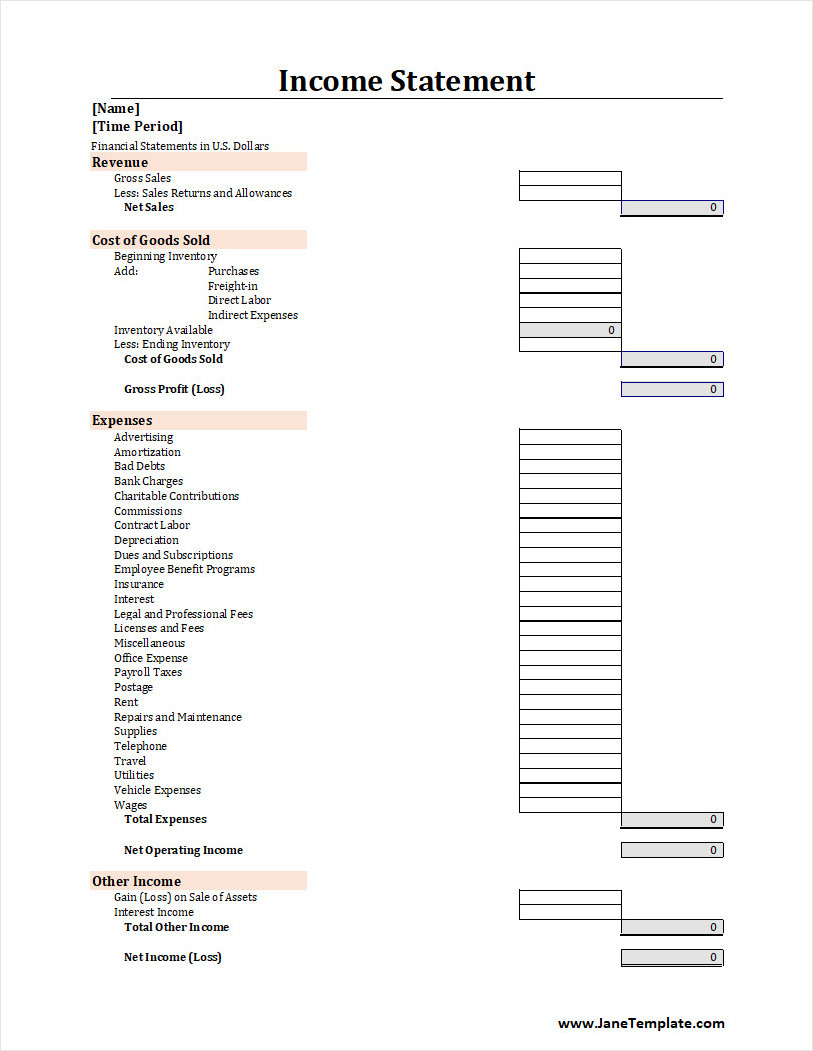
Income Statement Template
An income statement is a useful tool for tracking revenue, expenses, and net profit over a specific period. It helps businesses evaluate financial performance, identify trends, and make informed decisions.
To manage your finances with clarity, use our free income statement template and create organized, professional statements with ease!
Income Statement Template – Excel